Business Dashboard Overview
A business dashboard is a type of graphical user interface tool, which facilitates business users to track their business performance with the help of data visualization in a dashboard layout. It simplifies complex data sets with the help of drag-and-drop and auto-generated code for sharing your dashboard is commonly known as a business dashboard.
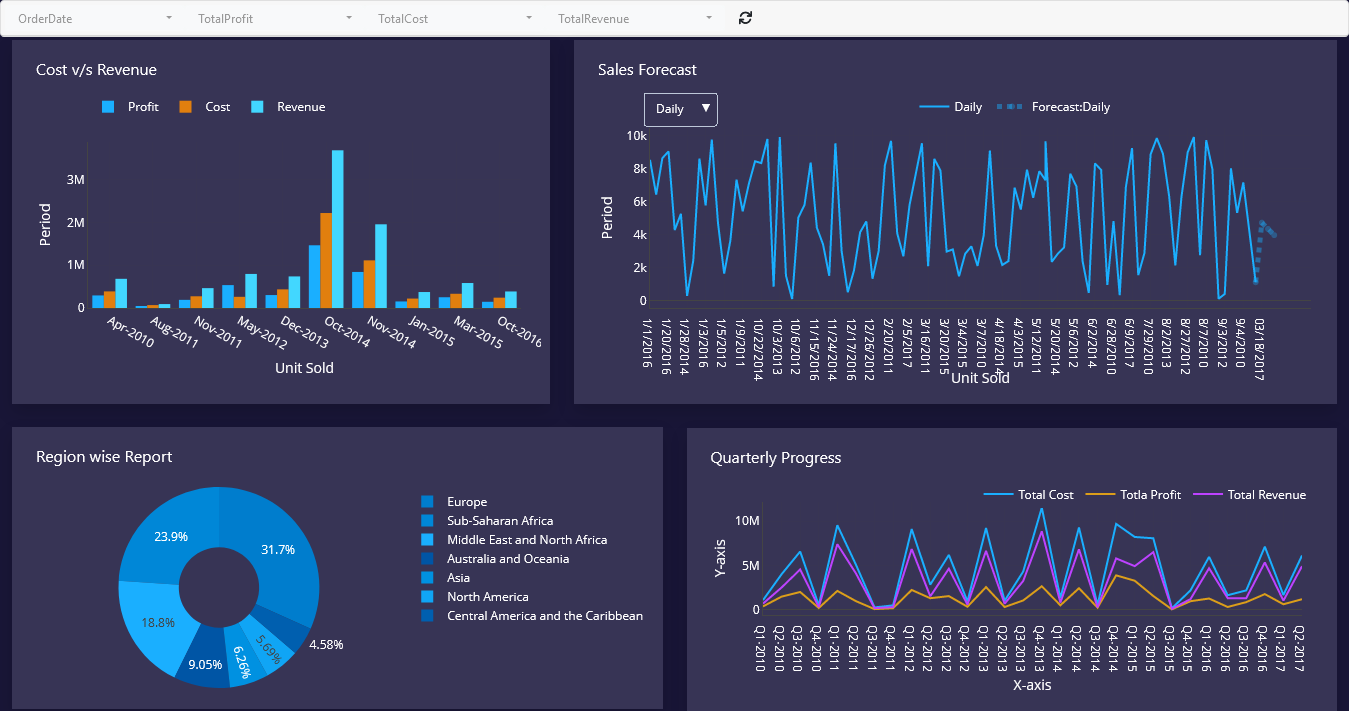
What is a Business Dashboard?
A business dashboard is a powerful drag-and-drop tool which doesn’t require any programming skill and that tracks and simplifies complex data query and gives quick insight of business performance to the business users.
The Evolution of Business Dashboards
Business dashboards have evolved over the last four decades. Businesses used decision support systems (DSS) to perform business intelligence tasks in the early 1970s. They were inspired by automobile dashboards, which show drivers the status of critical functions such as gasoline levels and speed.
These systems were revamped in the 1980s using a technology known as Executive Information Systems (EIS). Despite the fact that EISs were thought to be a technological advancement, users were plagued by long turnaround times for refreshing and managing data.
When the information age hit its stride in the 1990s, concepts like data warehousing and online analytical processing accelerated dashboard functionality.
Business dashboard use skyrocketed after KPIs became more widely adopted in the late 1990s. Dashboards were identified as a component of the Digital Nervous System.
Now consider the business intelligence dashboards available today: Dashboard visualization has evolved into an industry standard, widely used by analytics professionals and student and executives of global organizations.
Why do companies use business dashboards?
The main reason for using a business dashboard is to provide a comprehensive view of business performance. A business dashboard summarizes different sections of business with easy-to-understand in a graphical layout.
The Advantages of Business Dashboards
Businesses must make informed decisions quickly. This is where business dashboards can come in handy. Furthermore, they integrate enterprise business information to improve workflow management across business functions. The following are the advantages of business dashboards:
1. Enhance Decision-Making
The most significant advantage of a business dashboard is improved decision-making. It enables users to make informed business decisions by providing summaries of aggregated data. Data is not only easier to consume, but it can also be analyzed more quickly. For example, an advertising executive may want to assess the success of a national television ad campaign run by his company. A business dashboard can display brand awareness metrics over time on a line graph, along with the dates the campaign advertisements were broadcast. The executive could also see how that awareness corresponded to sales during the same time period. According to the data, the TV campaigns were a success and should be continued in the future.
2. Save Time
Business dashboards save users time by aggregating data from multiple sources and highlighting the most important KPIs. Without dashboards, organizations must manually compile and aggregate data from multiple sources. The manual method necessitates more resources than an automated dashboard and increases the possibility of human error. Automation frees up valuable time for more detailed analyses and increases employee satisfaction by eliminating mundane, repetitive tasks. According to Forbes, we generate over 2.5 quintillion bytes of data per day, with the last two years alone producing 90% of all data ever created. This volume of information can be overwhelming for any organization, but it can be prioritized to save time. Smart Goal-Setting.
Because the right data can be delivered at the right time, organizations can make more data-driven decisions with goal-setting. This results in more precise benchmarks and actionable goals at all levels of the organization. Throughout the quarter, executives can see how the business is performing in real time and make tactical pivots if they notice an objective isn't working. Goals and expectations can be adjusted as needed with new information. When data is visible throughout an organization, KPIs can be aligned with business goals to improve business processes.
3. Sharable Insights
The full implementation of an analytics platform provides visibility into KPIs across the enterprise. A finance department at a manufacturing company, for example, may want to see how marketing and sales affect revenue for budget planning purposes. A business dashboard provides real-time access to this data to anyone in the finance department. Leaders in an IT department may want to understand how their department's employee retention compares to the overall organization to determine if their management methods are effective in terms of employee satisfaction.
Business Dashboards Best Practices
1. Establish Dashboard Objectives
Each stakeholder's explicit objectives should drive the planning and design phases. For example, the sales department may request a high-level dashboard that allows them to dig down to specific regions and product SKUs. This type of dashboard is intended to assist sales leaders and executives in identifying the most effective items and top-performing salespeople in each location. Company resources can then be deployed accordingly, such as pushing marketing money into a lagging region or shifting messaging to correspond with demand in a certain region.
2. Maximize Perfection
A company dashboard is pointless without correct data. In fact, it might be harmful to the business because poor decisions will be made. As a result, correct data is essential for the success of a company dashboard. Data should be validated for accuracy at every stage of the implementation process, beginning with the design phase. Before adding data to the business dashboard, ensure that each data source is accurate. It should also be checked after the data has been cleaned or converted, and it is a best practice for any extract, transform, and load procedure (ETL). When the dashboard is finished, each stakeholder should review the data and examine it for accuracy on a regular basis during its existence.
3. Customize Views
Each stakeholder should have their own segmented view of the dashboard that is tailored to their individual objectives. A financial department, for example, would not benefit from reviewing ad text performance data for the marketing department. During the planning process, these requirements will be discovered. Platforms with various dashboards are ideal because they can serve multiple audiences. With the Dashboard Builder enterprise-grade business dashboards are produced that can meet this requirement. Because a single dashboard rarely pleases all stakeholders, distinct tailored dashboards for each stakeholder group may be preferable.
4. Enable Users to Dig Deeper
The finest dashboards provide users with a high-level picture of the data and allow them to drill down for more detail by selecting data segments. A sales analytics dashboard, for example, may display deals by location, and a user could drill down to discover which products sold well in each region and which salespeople performed best. To keep the dashboard from becoming cluttered, just provide the most relevant data for each display. This top-down method is user-friendly and should be used for sophisticated capabilities.
5. Apply filters
Users can streamline how they display data in business dashboard visualizations by adding filters. This enables users to rapidly identify pertinent insights and prevents them from pulling excessive data that can slow down performance. Self-service data discovery includes filters, which help users engage graphically with datasets. Users can utilize filters to slice and dice data to discover novel business patterns.
Case Studies: Business Dashboard Success
1. Financial Dashboard
Users can get a financial overview of a business on financial dashboards. An overview of revenue throughout time and business units is displayed in the example above. Additionally, the user can choose between views that are tailored to cost, cost of sales, operating costs, and net profit/loss. They can also dig deeper and view the financial performance of each business unit.
2. Sales Dashboard
An overview of sales over time by location, product SKU, and store can be seen in a retail sales dashboard. These are beneficial for merchants with numerous locations and a wide variety of goods. Executives can immediately identify which areas are performing the best and which ones would require further care. To promote innovation, these dashboards can also display the effectiveness of pilot projects.
3. Dashboard for social media
Business dashboards are used by social media managers to track the effectiveness and user engagement of each social network, including Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, and Instagram. Data from all of these channels are combined in a dashboard, which offers insightful information about how and by whom messaging is viewed. Future social media posts can be better targeted based on this data and what topics get the best reactions.
What are the various types of business dashboards?
There are mainly three types of business dashboards available.
- Operations Business Dashboard: An operational business dashboard is a reporting tool that is used to monitor business processes that frequently change and to track the current business performance of KPIs.
- Strategic Business Dashboard: A strategic business dashboard is a reporting tool that is used to monitor the status of key performance indicators (KPIs), and are typically used by business executives such as CEO, CFO, CIO, etc.
- Analytics Business Dashboard: An analytical business dashboard is a reporting tool that is used to analyze huge volumes of data set to allow users to investigate trends, predict outcomes, and discover insights.
Type of business dashboard software
Dashboard Builder is available on both delivery modules ON-PREMISE download and install directly on your computer OR use ONLINE. Following is an overview of all types of dashboard builder available for you.
- On-premise: business dashboard software is installed directly on computer having Windows, Linux and Ubuntu or any other platforms support Apache, Nginx etc. Dashboards are managed locally and typically published via exporting as a PNG or generating PHP code for publishing your dashboard.
- Online Cloud based: The online business dashboard software gives you the freedom to access your dashboard from anywhere. It generates universal HTML code, enables you to share your dashboard to any website to boast impressive functionality and feature-depth in a lightweight package.
- On mobile: The business dashboard Software is responsive and accessible on any mobile device such as a smartphone or tablet. It’s automatically responds to the environment based on media's screen size, platform and orientation.
All of these charts are responsive that means the KPI dashboard responds to the media's screen size, platform, and orientation to render the KPI dashboard to fit on a variety of devices such as MS Window, mobile phones, tablets and PC’s screen sizes.
Business dashboard examples
Business dashboard lets you focus and align your entire business on a single glance to improve your most important business metrics. Following are the topmost important business dashboard examples are designed to make your business KPIs unmissable on a screen so that you can see how different sections of your business performing and prioritize work to improve performance.
(If you want to read more about what should be included in your business dashboard, see this article.)
- Business dashboard for sale
- Business dashboard for marketing
- Business dashboard for Financial Management
- Business dashboard for startup
- Business dashboard for supply chain
- Business dashboard for warehouse
- Business dashboard for Accounts receivables
- Business dashboard for HR
- Business dashboard for Performance Analysis
- Business dashboard for operations
What Business Dashboard Software Solution Is Best?
Companies have a wide range of dashboard options to select from, but the ideal software will rely on their unique requirements.
1. FREE business dashboard
The business dashboard is available for free online, and the on-premises software includes many of the same support resources as the commercial license. The free version of Business Dashboard is ideal for industrial-oriented dashboard and analytics. The business dashboard software free version also be found on GitHub under this license for Business dashboard Open Source Community. If you require additional capabilities, such as commercial use, consider our commercial license.
2. Individual Uses
A basic business dashboard solution is perhaps the best if the dashboard will only be utilized by an individual. The basic edition of the dashboard tools are available for MySQL, SQLite, Google and Excel that may be used individually and shared. Users of Excel may transfer data into spreadsheets with ease, while more technically inclined users can set up links to external sources.
3. Small Businesses
Depending on their needs, small businesses can choose a cost-free or more sophisticated solution. Smart companies that priorities analytics may employ a on-premises business dashboard solution using a public domain to share a single source of truth. If teams are spread out over various sites, this is extremely crucial. A small e-commerce business might, for instance, have a team responsible for operations in the United States but outsource development and manufacturing. In this case, a cloud-based solution will enhance the business process for analytics and keep everyone updated.
4. Enterprise Businesses
In order to enhance all business processes, large businesses actually require a contemporary business intelligence platform that can be integrated with their IT systems. When a business wants to provide dashboard functionality, data governance and security become imperatives. Advanced analytics, business mobility, and customization are additional features of an enterprise solution.
Dashboard Builder provides Windows Desktop version, a powerful data analytics tool for individuals. People can link data to the tool and instantly generate dashboards. Advanced analytics features like regression analysis and predictive modelling are also included.